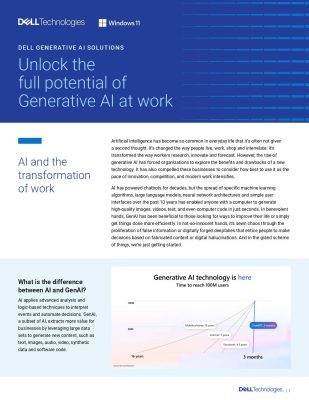
Highlights:
- Microsoft’s researchers state that SpreadsheetLLM employs a novel approach to encode spreadsheet contents into a format that LLMs can more effectively handle.
- SpreadsheetLLM has the potential to automate tedious spreadsheet tasks like data cleaning, formatting, and aggregation.
Microsoft Corp. researchers have recently unveiled an experimental artificial intelligence model named SpreadsheetLLM. Microsoft’s SpreadsheetLLM helps to design and operate spreadsheets like Excel and Google Sheets.
As described in a July 12 research paper on Arxiv.org, the model is intended to address the challenges of applying AI to spreadsheets. These tools, which are extensively used in the business world, have been difficult for large language models to handle effectively.
Microsoft’s researchers state that SpreadsheetLLM employs an innovative method for encoding spreadsheet contents into a format more accessible for large language models. This approach enables the models to effectively “reason over spreadsheet contents.”
The researchers emphasized the urgent need for advancements in this specific area of AI. Spreadsheets are used for a wide range of tasks, spanning from simple data entry and analysis to complex financial modeling and decision-making. However, current large language models (LLMs) find it challenging to comprehend and reason over spreadsheet contents due to their highly structured data, complex formulas, and references.
SpreadsheetLLM reportedly overcomes this issue by encoding spreadsheet data in a way that is more accessible for large language models, allowing them to understand it better.
To achieve this, the researchers developed an innovative encoding mechanism called SheetCompressor. This mechanism preserves the structure and relationships of the data while ensuring it is accessible to large language models. Notably, SheetCompressor can compress the data by up to 96%, enabling LLMs to manage large datasets within their token limits.
The researchers also highlighted another feature known as “structural anchor extraction,” which identifies the critical rows and columns defining table structures. Moreover, “inverted-index translation” effectively encodes cell contents and addresses to reduce redundancy, while “data format-aware aggregation” groups cells with similar formats, further optimizing token usage.
In their experiments, the researchers discovered that SpreadsheetLLM delivered impressive results in a spreadsheet table detection test, outperforming existing methods by 12.3%. Furthermore, it exhibited strong performance in tasks involving answering questions based on spreadsheets.
SpreadsheetLLM was integrated with several well-known LLMs, including GPT-3.5, GPT-4, and Llama 2. The tests demonstrated that it significantly improved these models’ capabilities in spreadsheet understanding tasks. For example, GPT-4 achieved a table detection score of 78.9%.
According to the researchers, SpreadsheetLLM remains an experimental model with certain limitations, particularly with more complex spreadsheet formats. However, they see significant potential in its capabilities. For example, they envision its application in automating routine data analysis to derive insights and recommendations from spreadsheet contents. Enhancing LLMs’ understanding of spreadsheets, enabling them to answer questions and even generate new spreadsheets based on natural language prompts, introduces new possibilities in AI-driven data analysis and decision-making.
SpreadsheetLLM also aims to improve the accessibility of spreadsheets for human users, many of whom find it challenging to navigate the more advanced features of tools like Excel. A significant hurdle in working with spreadsheets is mastering complex formulas for data manipulation. However, SpreadsheetLLM could enable users to manipulate data through natural language commands, potentially simplifying the process.
Lastly, according to the researchers, SpreadsheetLLM has the potential to automate tedious spreadsheet tasks such as data cleaning, formatting, and aggregation.
Holger Mueller, an analyst at Constellation Research Inc., emphasized the significance of the research, noting that Excel spreadsheets underpin much of the world’s business operations. He stated, “It’s vital for Microsoft to be at the forefront of this push to make Excel spreadsheets more accessible through AI. Verbal access to spreadsheets provides massive value, both for creating and analyzing Excel files.”
Mueller also pointed out that AI has the potential to democratize spreadsheet usage, making it accessible and easy for anyone to use. He predicted, “If Microsoft can nail this properly, it will not only secure the future of Excel but change the future of work as we know it.”
Currently, SpreadsheetLLM remains solely a research project, and Microsoft has not disclosed any plans to develop it into a commercial product. However, it’s conceivable that this research could lead to the development of a “Copilot for Excel” type of tool in the future.