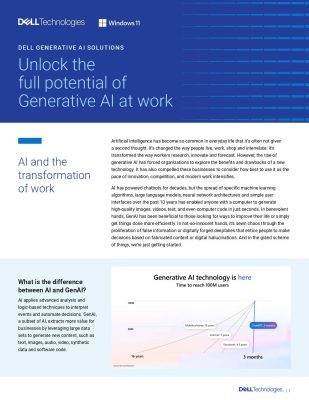
Highlights:
- The ACE LLM family is based on pre-existing fundamental model designs like Llama 2 from Meta Platform Inc., GPT-3.5 Turbo from OpenAI LP, and MPT from MosaicML.
- The lightweight seven billion parameter size of ACE LLM makes it simpler to deploy and fine-tune, and it may be scaled up to a 70 billion parameter size for situations that require greater precision.
Gupshup Inc., a conversational engagement platform for marketing and support automation, announced a new family of domain-specific generative AI LLMs. These models are tailored for customer support, marketing, commerce, human resources, information technology, and enterprise business operations.
The new domain-specific models, dubbed ACE LLM, let business users create software that can draw on internal business knowledge to create conversational experiences that blend natural language with industry-specific knowledge. These models provide more accurate human-like responses and have a greater speed and scope for answering industry-specific queries while performing knowledge work than other models on the market. This is due to their industry-specific tuning.
The ACE LLM family is based on pre-existing fundamental model designs like Llama 2 from Meta Platform Inc., GPT-3.5 Turbo from OpenAI LP, and MPT from MosaicML. However, it has been customized to meet the demands of various functions for different industry usage. It can be adjusted, for instance, to reflect the specific vocabulary, needs, and functional requirements of banking, retail, utilities, and more.
Beerud Sheth, Chief Executive and Co-founder of Gupshup, reported, “Our conversations with brands have led us to understand that there’s an immense interest in adopting generative AI solutions. However, issues such as cost, security, data residency etc. have acted as deterrents holding them back from exploring such solutions. ACE LLM addresses all these issues, enabling enterprises to capitalize on the transformative power of generative AI.”
Foundational LLMs produce responses that are reasonably human-like on several themes since they have been trained on a wide range of online text. Industry-specific requirements, however, are neglected. Customers and employees in the industry require highly specialized knowledge about goods or services, which necessitates skill in the nuances, language, and jargon that are appropriate for their market.
Sheth stated, “Business conversations need to meet a higher standard of accuracy, context, and relevance.” Gupshup’s ACE LLM effectively gives corporate business customers an industry-specific expert assistant by giving them access to the power of domain-specific models. “They give enterprises a huge head start in building AI-powered conversational experiences. A non-AI world analogy that explains this specialization would be one of a neurologist who is vastly more adept at handling issues of the brain than a general physician.”
A generic LLM, which was trained on a wide range of irrelevant data from the internet to simulate human-like dialogue, would find it difficult to distinguish between various sorts of financial statements. A banking-specific LLM, however, would enable a much more informative discourse based on knowledge of the industry and internal corporate data and promptly and precisely produce a response based on its fine-tuning.
This family of models has a leg up on generic foundational models due to its superior comprehension of internal concepts, terminology, and context, which can be fine-tuned with ACE. It has a superior system for specific responses and can provide precise responses and efficient conversations to consumers and employees who require accurate responses based on the information they are pursuing.
The company incorporated safeguards into the model to guide its behavior, ensuring a concentration on appropriate replies. Users can modify the company’s knowledge base to suit the desired tone, precision, and control over data sources when utilized in conjunction with the company’s knowledge base. Additionally, users can access a dashboard for auditing, a teach-mode for non-generative responses, automated testing, and analytics for keeping track of and tweaking the model.
This increases confidence in the model’s responses. An industry-specific LLM is a more dependable source when it produces accurate and pertinent content. A generic model is more likely to create less detailed information and hedge its responses when it cannot find the correct feedback.
The lightweight seven billion parameter size of ACE LLM makes it simpler to deploy and fine-tune, and it may be scaled up to a 70 billion parameter size for situations that require greater precision. The LLM can produce text in approximately 100 different languages, including English, Bahasa, Arabic, Mandarin, Hindi, Spanish, Portuguese, French, and German. The Gupshup public cloud offers choices for geo-specific data residency or enterprise-private clouds with great scalability where the ACE LLM models can be deployed.
As for the future of industry-specific LLMs, Sheth explained that they are on the rise and represent a significant stride forward for conversational AI. “The ascent of vertically trained LLMs represents a significant influence on the evolution of language models. These specialized models offer vast potential in domains where precision, context, and specialized knowledge hold utmost importance,” added Sheth.