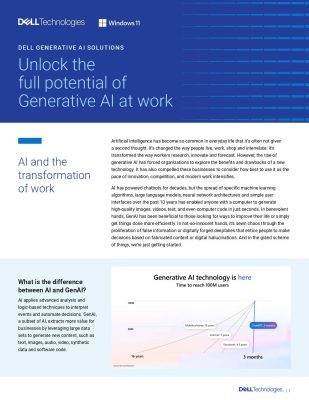
Highlights:
- Nvidia used pruning and distillation, two machine-learning techniques, to build Mistral-NeMo-Minitron 8B.
- A day after Microsoft released three of its own language models as open-source, Mistral-NeMo-Minitron 8B was released.
Nvidia Corp. launched Mistral-NeMo-Minitron 8B, a lightweight language model that can beat comparably sized neural networks over a range of tasks.
Hugging Face is offering the model’s code under an open-source license. Its release occurred one day after Microsoft Corp. released a number of its open-source language models. The new models are intended to function on devices with constrained computing power, much like Nvidia’s latest algorithm.
Nvidia introduced the Mistral-NeMo-Minitron 8B, a reduced-scale variant of the Mistral NeMo 12B language model. The latter algorithm was created in partnership with a well-funded artificial intelligence business called Mistral AI SAS. Nvidia used pruning and distillation, two machine-learning techniques, to build Mistral-NeMo-Minitron 8B.
Pruning is the process of eliminating extraneous code from a model’s code base to lower the hardware requirements. A neural network consists of numerous artificial neurons or little code bits that carry out a single, somewhat easy set of operations. Specific code snippets can be eliminated without substantially lowering the AI’s output quality since they don’t process user requests as actively as others.
Following the trimming of Mistral NeMo 12B, Nvidia proceeded with the project’s distillery phase. In the process of distillation, engineers transfer the AI knowledge to another neural network that is hardware efficient. The Mistral-NeMo-Minitron 8B, which made its debut recently and has four billion fewer parameters than the original, was the second model in this instance.
Developers can also decrease the hardware requirements of an AI project by starting from scratch and training a fresh model. Compared to that method, distillation has a number of advantages, most notably superior AI output quality. Because less training data is needed, reducing a large model into a smaller one costs less.
Nvidia stated that its pattern of syncing distillation and pruning techniques during development majorly enhanced the effectiveness of Mistral-NeMo-Minitron 8B. “The new model is small enough to run on an Nvidia RTX-powered workstation while still excelling across multiple benchmarks for AI-powered chatbots, virtual assistants, content generators, and educational tools,” said Nvidia Executive Kari Briski.
Nvidia unveiled Mistral-NeMo-Minitron 8B, a day after Microsoft launched three language models as open-source. They were created considering hardware efficiency, much like Nvidia’s new algorithm.
The smallest in the range is the Phi-3.5-mini-instruct model. It can consume large business documents since it has 3.8 billion parameters and can process prompts with up to 128,000 tokens of data. Microsoft’s benchmark test found that Phi-3.5-mini-instruct can outperform Llama 3.1 8B and Mistral 7B, which have about twice as many parameters for some tasks.
Recently, Microsoft released two more language models as open-source projects. The first, Phi-3.5-vision-instruct, is a Phi-3.5-mini-instruct variant that can carry out image analysis tasks, including providing an explanation for a chart that the user uploads. It was released concurrently with Phi-3.5-MoE-instruct, a much larger model with 60.8 billion parameters. A tenth of those parameters activate upon user entry, reducing the hardware required for inference.