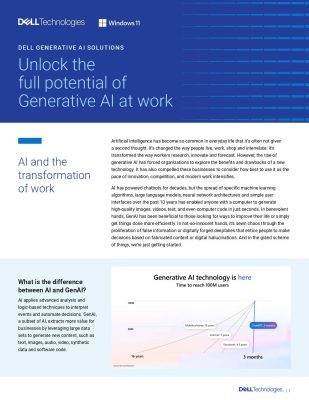
Highlights:
- According to a prominent media outlet, sources indicate that the investment is anticipated to exceed USD 400 million.
- The company’s website also outlines its intention to develop a customized stack, or software toolkit, for AI training purposes.
A startup based in Paris, Poolside plans to launch a large language model for developers and is reportedly in discussions to secure a funding round in the nine-figure range.
According to a prominent media outlet citing sources, the investment is anticipated to exceed USD 400 million. Insider reports suggest that Bain Capital Ventures and DST are in talks to lead the funding round jointly. This funding is projected to value Poolside at USD 2 billion.
Poolside is headed by CEO Jason Warner, who previously served as the Chief Technology Officer at GitHub. The company’s Co-founder, Eiso Kant, previously founded Athenian, a developer tooling startup acquired by the Linux Foundation in 2023.
Reportedly, Poolside relocated its headquarters from the United States to Paris in August last year and secured an initial funding round of USD 126 million around the same period. Bain Capital Ventures, a potential co-lead investor in the company’s upcoming raise, was reportedly part of this round, along with Redpoint, Felicis, and several other backers.
According to its website, Poolside is creating an LLM tailored for coding tasks. The company intends to differentiate its model from other AI systems focused on programming by employing a training method in terms of reinforcement learning based on feedback from code execution. Poolside explained that this method will allow the LLM to “improve by completing millions of tasks in tens of thousands of real-world software projects.”
The company’s website also outlines its intention to develop a tailored software toolkit for AI training. These toolkits generally incorporate functionalities to assist researchers in managing datasets for machine learning projects. Additionally, AI training software often automates tasks such as evaluating the accuracy of newly developed LLMs.
Poolside emphasized on its website that it intends to prioritize the quality of training data in its development initiatives. The company added, “Synthetic data generation, while seemingly counterintuitive, works and works particularly well for code.” Synthetic data refers to information generated by AI to develop other neural networks.
Earlier this year, Poolside secured an agreement to lease AI training infrastructure from Australian data center operator Iren. The contract involves a cluster of 504 H100 graphics processing units, which were Nvidia Corp.’s flagship data center GPUs until a product line update last November.
Poolside’s immediate goal is to enhance developer productivity with its LLM, but its long-term roadmap extends beyond this. Future plans include training AI models enabling business users to create software, with ambitions to apply the reasoning capabilities of its language models to diverse fields.